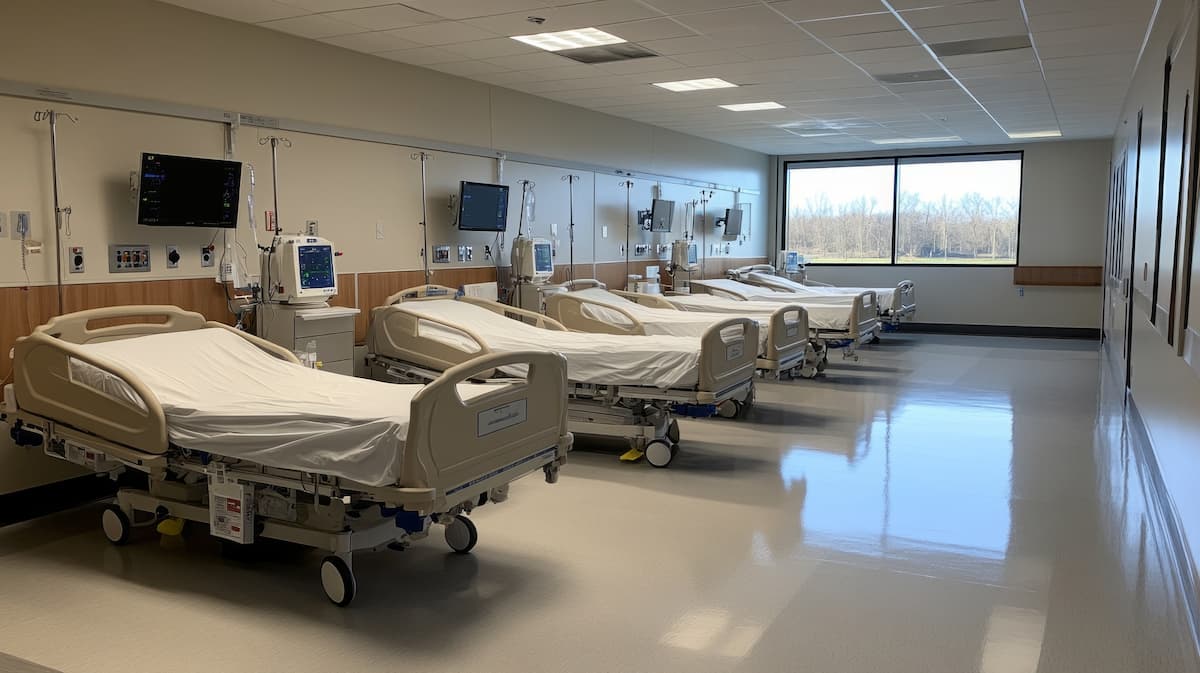
The United States is on track for a potential hospital bed crisis as occupancy rates continue to climb. According to researchers from UCLA, hospital occupancy is expected to rise from the current 75% to 85% by 2032. This increase pushes the system dangerously close to what experts define as a bed shortage, where hospitals struggle to accommodate patients efficiently.
The study, which analyzed hospital capacity trends using CDC data, found that the rising occupancy rate is not due to more hospitalizations but rather a 16% decline in staffed hospital beds. Workforce shortages and hospital closures many linked to private equity acquisitions have played a significant role in reducing available hospital space. Without intervention, this trend could lead to longer wait times, more medical errors, and preventable deaths.
Why Hospital Occupancy is Rising
For over a decade, U.S. hospital occupancy hovered around 64%. However, post-pandemic pressures have driven this number up to 75%, with projections reaching 85% within the next seven years. A hospital system operating at such high occupancy levels is vulnerable to surges from daily bed turnover, seasonal spikes in demand, and unexpected public health emergencies.
While hospitalizations have remained relatively stable, the available supply of staffed hospital beds has dropped by 16%. This decline is largely attributed to:
- Staffing shortages – A lack of registered nurses and support staff has forced hospitals to keep beds empty despite patient demand.
- Hospital closures – Some hospitals, particularly in rural areas, have shut down due to financial struggles, leaving fewer treatment options.
- Private equity-driven cost-cutting – Some hospital owners have closed or repurposed facilities to maximize financial returns, reducing overall bed availability.
At an 85% national hospital occupancy rate, many facilities would struggle to handle fluctuations in patient volume. Experts warn that this level of strain on the system could result in thousands of excess deaths each year.
The Consequences of an 85% Occupancy Rate
A hospital system running at 85% capacity faces significant challenges that impact both patient outcomes and medical staff efficiency. Potential consequences include:
Longer Wait Times in Emergency Rooms
High occupancy levels can cause significant delays in admitting patients, forcing many to wait hours or even days for a hospital bed. Overcrowding leads to patients being treated in hallways or waiting rooms, increasing stress for both staff and those in need of care.
Increased Risk of Medical Errors
A strained hospital system increases the likelihood of medication mistakes, misdiagnoses, and other in-hospital complications. Overworked staff may struggle to provide optimal care, leading to higher rates of preventable harm.
Greater Mortality Rates
According to UCLA researchers, if hospital occupancy reaches and sustains 85% or higher, the U.S. could experience tens to hundreds of thousands of preventable deaths annually. This includes deaths from conditions that might have been managed with timely hospital care but worsened due to delays in treatment.
How Hospitals Can Prepare for Rising Occupancy
To avoid a full-scale crisis, healthcare leaders and policymakers must take action to increase hospital capacity, improve staffing levels, and regulate financial practices that contribute to closures. The UCLA report recommends:
- Expanding the healthcare workforce – Addressing nurse and physician shortages by increasing medical training programs and improving working conditions.
- Regulating private equity in healthcare – Preventing cost-cutting measures that result in hospital closures and reduced patient care capacity.
- Improving hospital funding – Increasing reimbursement rates and financial support to prevent more hospitals from shutting down.
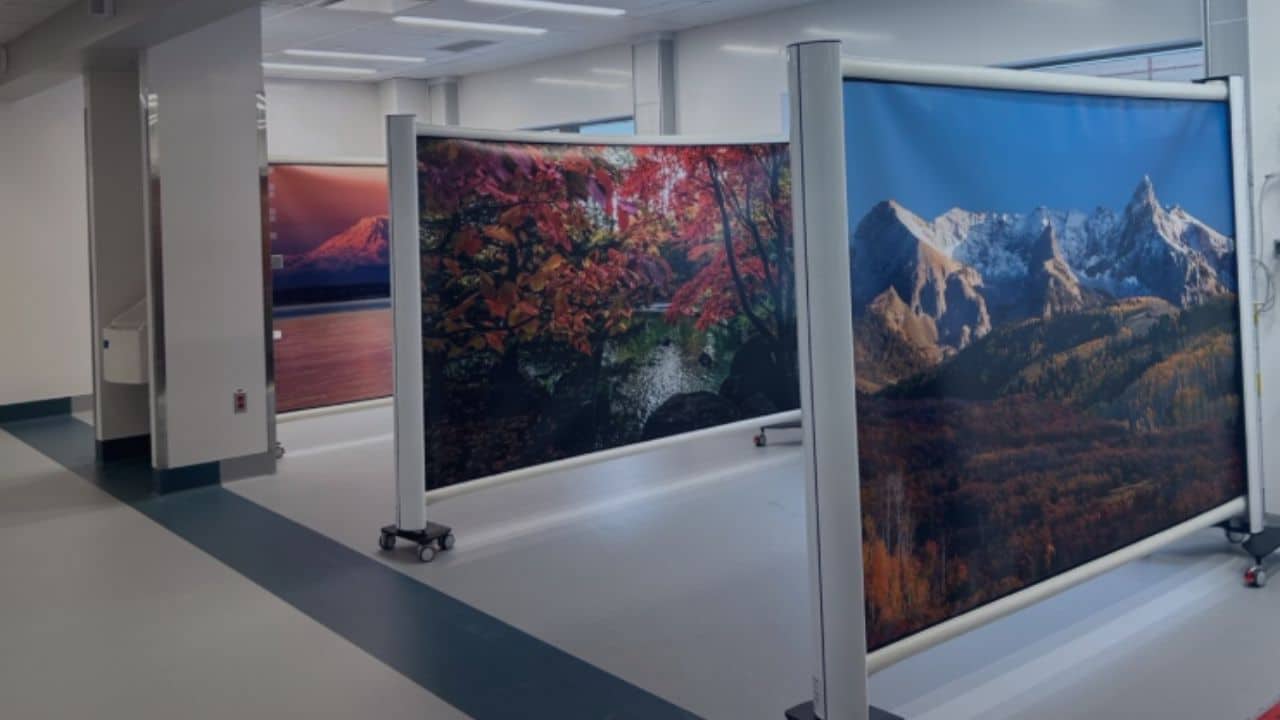
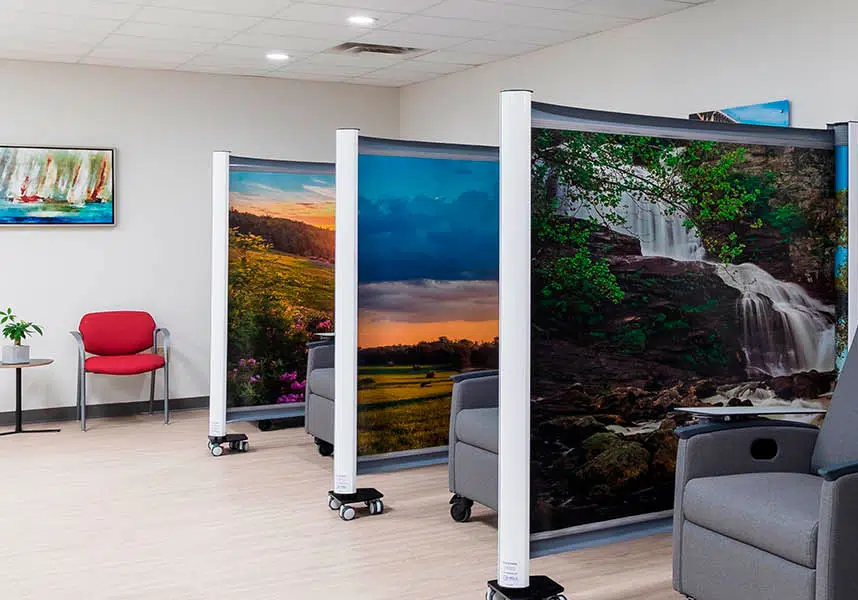
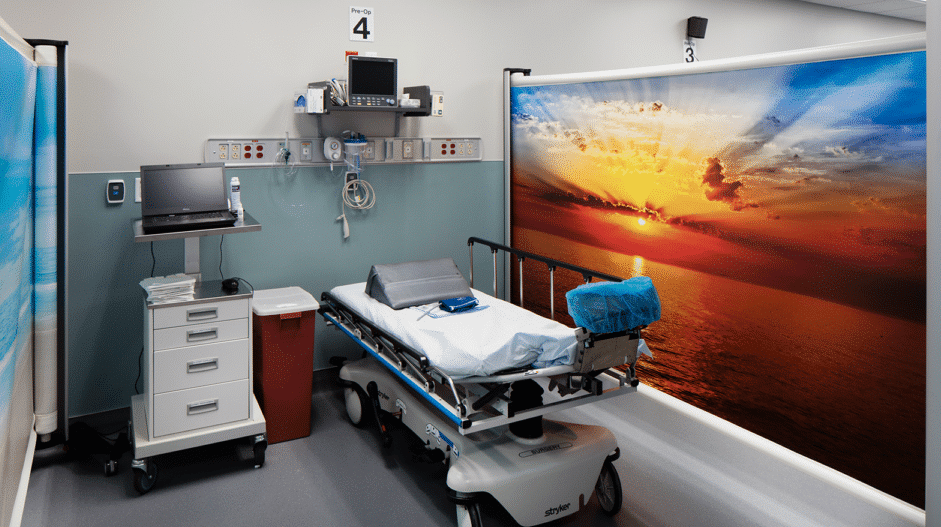
Enhancing efficiency with better space management – Using flexible privacy solutions like Rolascreen to optimize available space and accommodate more patients without requiring costly infrastructure expansion.
A Smarter Approach to Space Management
With U.S. hospitals expected to face even greater occupancy challenges in the coming years, flexible solutions that maximize available space will be critical. Rolascreen privacy screens allow hospitals to create temporary triage areas and patient spaces instantly, making them an essential tool in emergency preparedness.
Unlike traditional partitions, Rolascreen retracts completely when not in use, freeing up valuable space while still providing necessary privacy for patients. As hospitals struggle to adapt to rising patient demand, efficient space management will play a crucial role in maintaining quality care.
The Future of U.S. Hospital Capacity
With hospital occupancy expected to reach critical levels by 2032, urgent action is needed to prevent unnecessary delays, errors, and fatalities. Addressing staffing shortages, improving financial policies, and optimizing hospital space with adaptable solutions will be key to ensuring patients receive the care they need, when they need it.
Contact Rolascreen today to learn how hospitals can improve space management and prepare for the future.